Why is it important to perform an Axis Alignment?
Shaft alignment refers to the process of properly adjusting and positioning the shafts of both the engine and the industrial asset or machinery. This procedure seeks to ensure that rotating components are perfectly aligned to optimize their performance and prevent operational problems.
This practice, within predictive maintenance, is not only recommended, it is a necessity to maintain optimum equipment performance. When the axes are aligned, the overall efficiency of the system is improved and not budgeted costs are avoided.
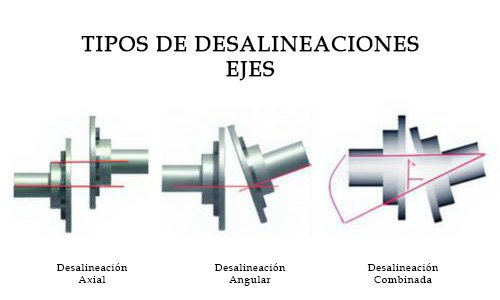
What are the main types of misalignment?
Angular misalignment: occurs when the shafts of a rotating equipment are not perfectly aligned in an angular plane. In other words, the axes do not form a correct angle to each other. This results in deviations and shifts in the relative orientation of the components.
Axial misalignment: refers to the condition in which the axes are not perfectly aligned along a common line. In this case, the axes do not follow a parallel trajectory and present an undesired displacement.
Combined Misalignment: occurs when shafts are not optimally aligned in multiple planes, including both axial and angular alignment. In this scenario, the misalignment affects both the orientation along the centerline and the angle between the axes, creating a more complex problem.
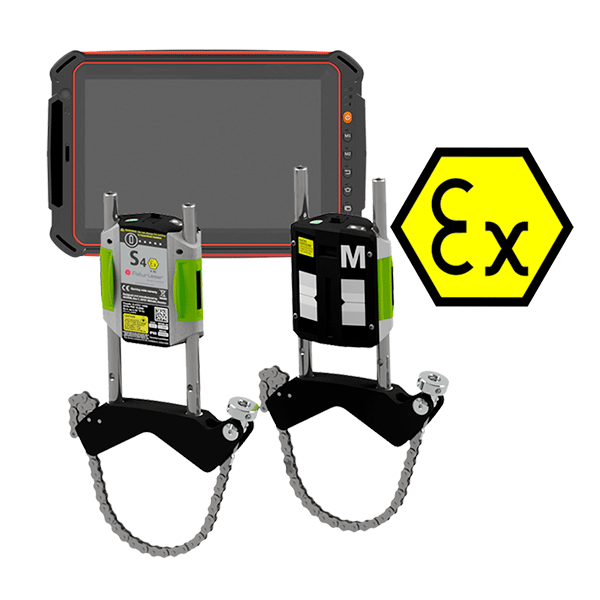
Depending on the position of the rotating machinery, shaft alignment is performed in horizontal or vertical direction. The AT-100 aligner is a complete equipment that provides high measurement flexibility and is ideal for shaft alignment work from basic to expert level, it is exclusive for horizontal shafts.
The AT-200 and AT-400 aligners include all of Acoem’s technology and are perfect for horizontal and vertical shaft alignment, featuring intelligent sensors for superior measurement performance and precision alignment.
The EXO aligner’s Atex technology not only performs high-precision horizontal and vertical alignments, but also allows measurement in areas where dust or gases accumulate that could cause an explosion.
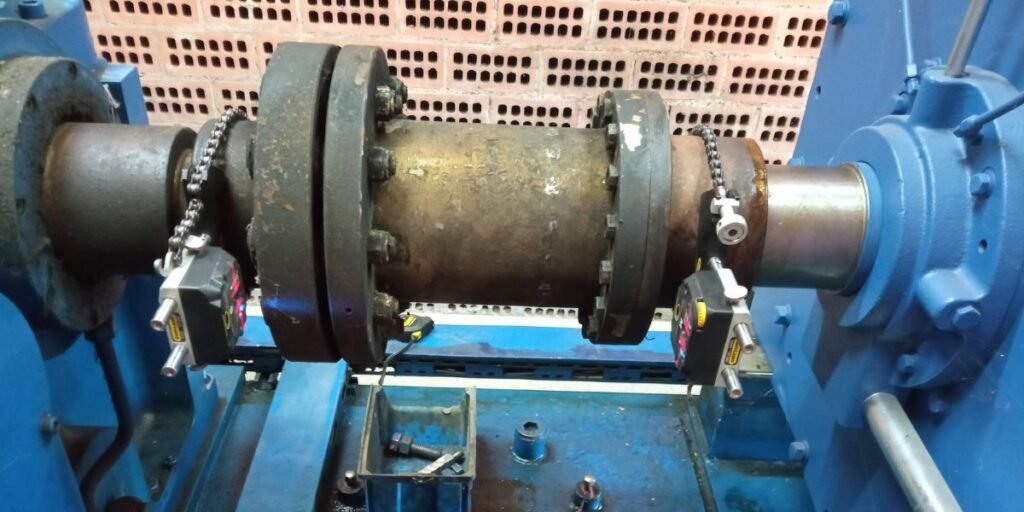
Reasons to perform a Shaft Alignment
Equipment Wear Prevention: Misalignment of shafts increases uneven wear of rotating machinery components and reduces equipment life.
Vibration Reduction: Misalignment can generate unwanted vibrations in machinery, which negatively affects, stability, accuracy, quality and system performance. Correcting it contributes to a safe working environment.
Loss of Energy Efficiency: The additional friction caused by misalignment increases the load on the motor, leading to higher energy demand and consequently reduced energy efficiency.
Premature Bearing Failures: Bearings are particularly sensitive to misalignment and can experience premature failure.
Avoiding Unscheduled Downtime: Performing regular alignments minimizes the likelihood of unscheduled downtime, ensuring continuous production without additional costs.
Compliance with Industry Regulations: Maintaining shaft alignment according to industry regulations and standards ensures compliance with safety, quality and performance requirements established by authorities and regulatory bodies.
What equipment do you need? Learn about our range of state-of-the-art shaft aligners here.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Keep up to date with all the latest news on predictive maintenance and reliability!







